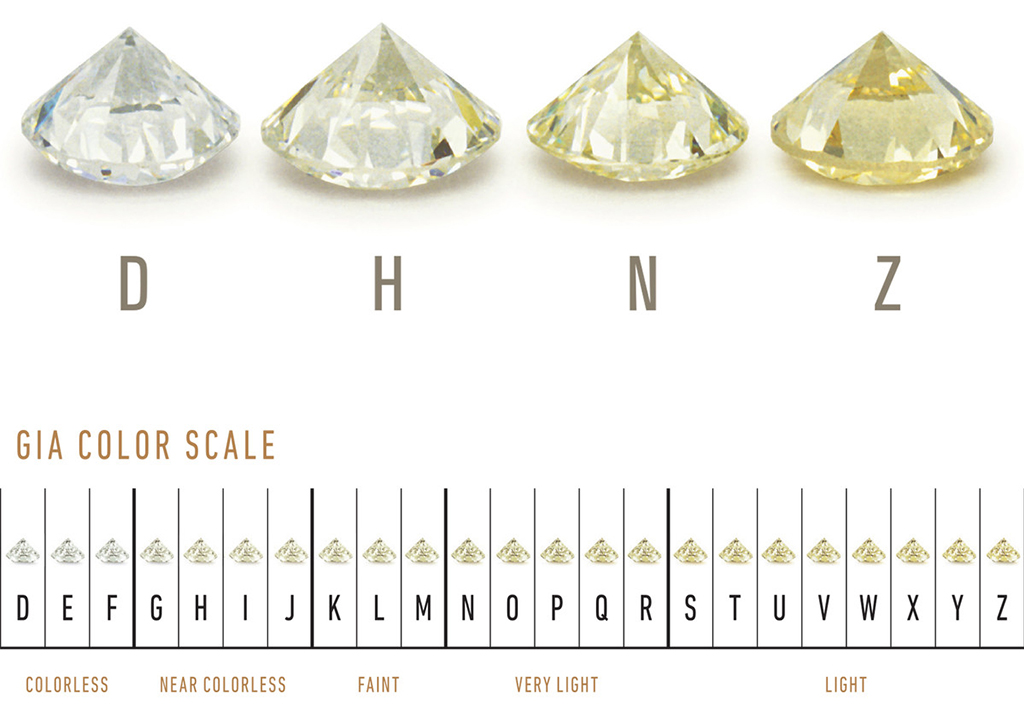
Color
Colorless diamonds are graded on a color scale from D-Z. A diamond which receives a color grade of D is absolutely colorless and is considered to be the best color-grade a colorless diamond can receive. As we progress down the towards Z ,the diamonds start to exhibit a tinge of yellow visible face-up, with Z exhibiting the most prominent tinge of yellow color. Look here
Once a diamond goes beyond the Z color range, it becomes a fancy-colored diamond, starting with Fancy Light and as we move to more saturated levels of color the scale reads Fancy, Fancy Intense, and Fancy Vivid. The more saturation a diamond has in the fancy-color range usually the higher value it commands.
Color

Carat

Carat
Carat is the unit of measure that expresses the weight of the diamond. This is an absolute figure and one carat is equivalent to 0.2 grams. This number is usually expressed to two decimal places. Examples would be 0.50 carats, or 1.50 carats.
Clarity
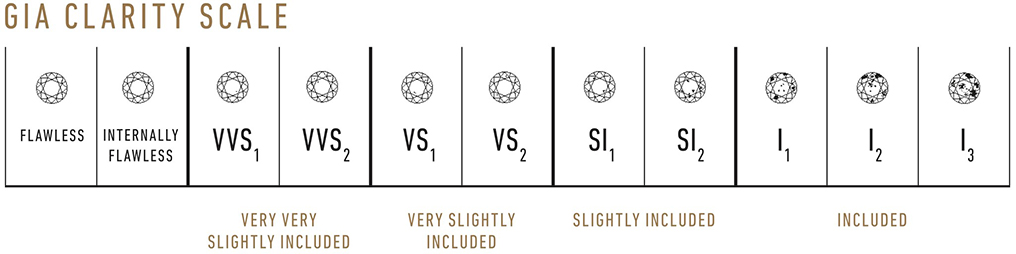
Clarity is defined as a gemstone’s relative freedom from imperfections, known as inclusions or blemishes. Inclusions are concealed within a diamond, though they can in fact reach to the stone’s surface, whereas blemishes are confined to a stone’s surface. Inclusions are usually more visible under 10X magnification, and therefore have a larger impact on a stone’s clarity grade than blemishes. Many in the trade look at inclusions as the stones “birthmarks,” as it is extremely unlikely that two stones would exhibit the same clarity characteristics in the same location, helping to identify each stone from one another. Clarity grades range from “Flawless,” which implies a lack of any inclusions, down to Included 3 (written as I3) which implies the lowest clarity grade for a gem quality stone.
Clarity
Cut
Cut
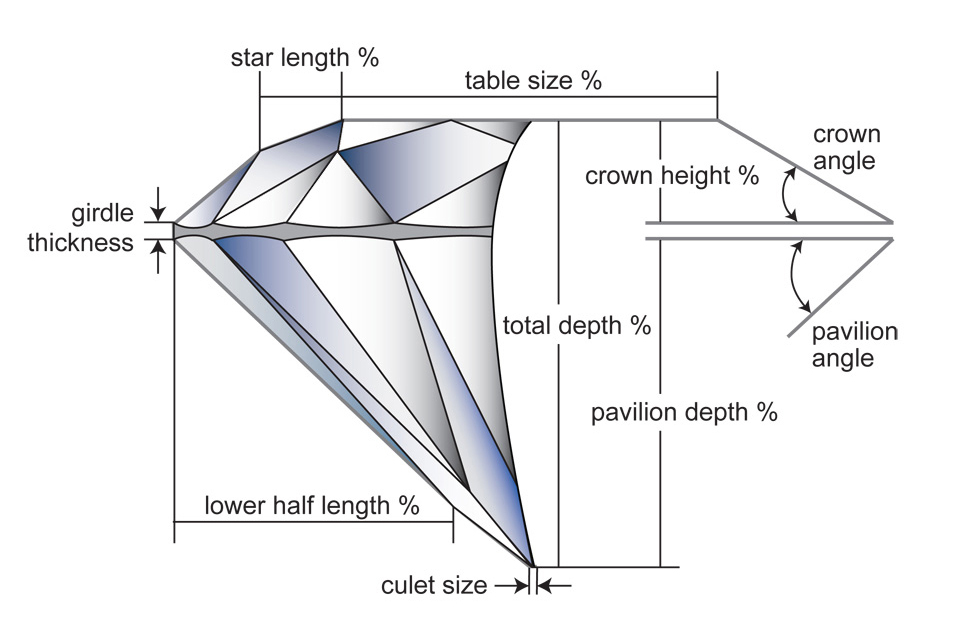
A diamond’s cut speaks to two factors: a polished diamond’s proportions and shape. The proportions are a polished diamond’s angles and relative measurements and the relationship between them. This has a direct correlation to the way the faceted diamond interacts with light, which translates directly to the stone’s beauty. A cut grade only exists for Round Brilliant Diamonds and ranges from Excellent (EX), Very Good (VG), Good (G), Fair (F), to Poor (P).
The second factor influencing diamond’s cut grading is the shape. Shapes fall under two category headings, Round Brilliant Diamonds and Fancy Shape Diamonds. Fancy Shape Diamonds encompass all diamond shapes that are not Round Brilliant and popular ones being Cushion Cut, Pear Shaped, Marquis, Oval, Radiant, and Emerald.

